German chamomile, Matricaria recutita, is sufficiently different from the also drinkable Roman chamomile that botanists don’t classify them under the same genus. (A genus is group of similar species.) Both plants, however, have flowers typical of the Compositae or Asteraceae family, a group of genera that also includes dandelions, sunflowers and lettuce.
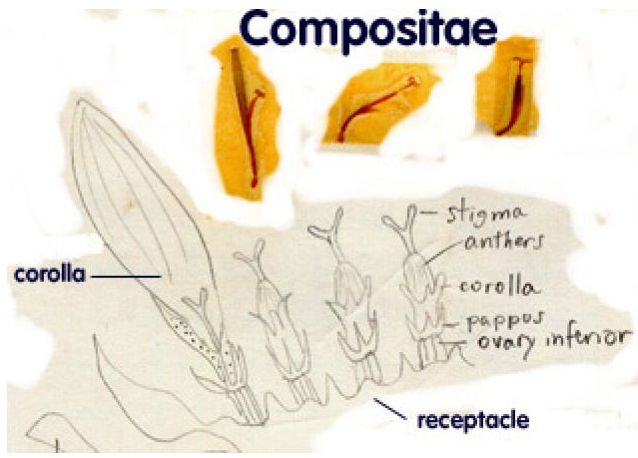 What looks like a single flower is actually a composite of tiny, identical flowers, giving members of this family the power to produce a greater number and wider variety of seeds. My diagram shows the basic structure of such flowers; note, however, that the pictures of the actual samples shown are from another member of the Compositae family. German chamomile flowers are a little smaller than the ones I preserved.
What looks like a single flower is actually a composite of tiny, identical flowers, giving members of this family the power to produce a greater number and wider variety of seeds. My diagram shows the basic structure of such flowers; note, however, that the pictures of the actual samples shown are from another member of the Compositae family. German chamomile flowers are a little smaller than the ones I preserved.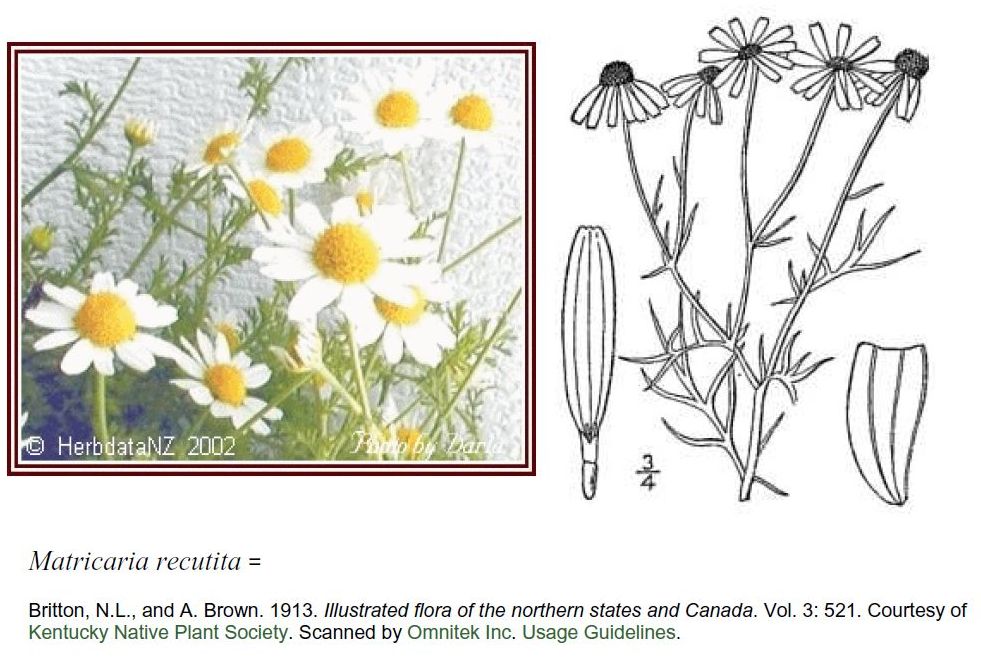 2. Traditional Uses
2. Traditional UsesTraditionally, the essential oil obtained from chamomile flowers has been used to treat inflammations of the skin and mucosa. It is also inhaled to treat nasal catarrh, inflammation and irritation of the respiratory tract. The tea is drunk to treat
flatulent nervous dyspepsia, gastritis, diarrhea, travel sickness and mild anxiety. Is there any evidence that chamomile has any medicinal properties.
3. Evidence
In human studies, anti-inflammatory, antiseptic, antispasmodic effects have been attributed to compounds known as flavanoids and sesquiterpenes. One of the sesquiterpenes, chamazulene, has been reported to have antioxidant activity in a 2000 study on rapeseed oil. More recently, in December 2004, the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry reported a study on chamomile chemistry. The authors used high resolution 1H nmr spectroscopy and other methods in what is known as a metabonic strategy. This technology tries to obtain meaningful results for nutritional interventions, which typically are complicated by many variables such as genetics, gender and environmental factors. The equivalent of 5 cups of chamomile tea (Matricaria recutita) were given to 14 volunteers for a period of two weeks. For a total of six weeks, their urine samples were monitored: two weeks prior to ingestion (to serve as a baseline) and also for two weeks after treatment to examine any potential lingering effects. The most significant result was that the volunteers excreted more
hippurate, glycine and an unknown metabolite.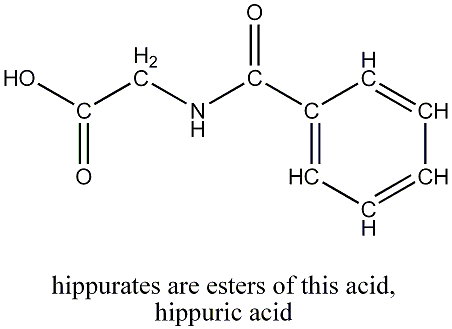
The levels of hippurate also were elevated in the post treatment period. Previous studies had revealed that hippurate levels fluctuate as different microbes battle it out within a rat’s gut. Since evidence exists for chamomile flowers’ antimicrobial activity, one possible explanation put forward by the authors is that the chamomile killed some bacteria in the intestines. Two weeks after treatment, different populations of microorganisms had still not reestablished the original equilibrium between themselves. They point out that this is significant since these intestinal bacteria have a serious impact on digestive absorption and on the immune system.
4. Other Molecules in Chamomile
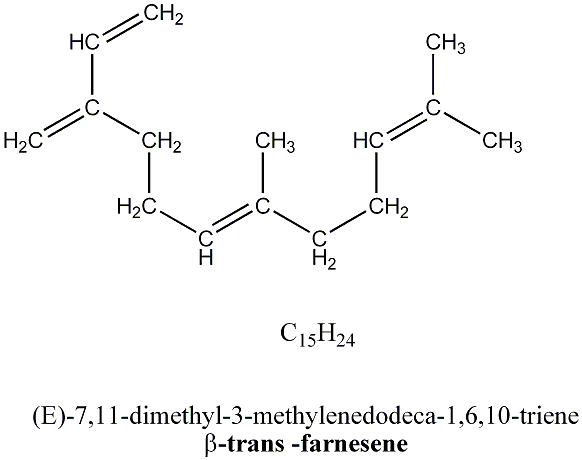 Beat trans- farnesene is a compound built up with 3 isoprene units (5 carbons), which are common building blocks of natural products. A similar compound(the alpha version) gives green apples their characteristic odour. The beta form that is found in chamomile is also found in other essential oils, and it's the chemical alarm messenger used by aphids when attacked.
Beat trans- farnesene is a compound built up with 3 isoprene units (5 carbons), which are common building blocks of natural products. A similar compound(the alpha version) gives green apples their characteristic odour. The beta form that is found in chamomile is also found in other essential oils, and it's the chemical alarm messenger used by aphids when attacked.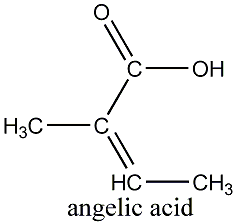 Angelic acid, a relatively simple molecule, tends to be more common in Roman chamomile. The esters of the compound have been used as a sedative.
Angelic acid, a relatively simple molecule, tends to be more common in Roman chamomile. The esters of the compound have been used as a sedative.One of science 2.0's featured writers pointed out that chamazulene is another compound found in Matricaria recutita.
 The molecule is a derivative of an azulene, the name given to the two ringed system shown here:
The molecule is a derivative of an azulene, the name given to the two ringed system shown here: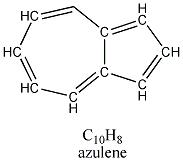 Azalenes are colored compounds and their derivatives are found in mushrooms and even in invertebrates. But what role does chamazulene play? It has anti inflammatory properties according to one published paper, which in its abstract dubbed chamazulene as a natural "ibuprofen"(Advil), an NSAID (non steroidal anti inflammatory drug).
Azalenes are colored compounds and their derivatives are found in mushrooms and even in invertebrates. But what role does chamazulene play? It has anti inflammatory properties according to one published paper, which in its abstract dubbed chamazulene as a natural "ibuprofen"(Advil), an NSAID (non steroidal anti inflammatory drug).References
1. United States Department of Agriculture http://plants.usda.gov
2. Wink and van Wyk. Medicinal Plants of the World. Timber Press. 2004
3. Wang,Y., Tang, H. A Metabonic Strategy for the Detection of the Metabolic Effects of Chamomile( Matricaria recutita L.) Ingestion. J. Agricultural and Food Chemistry
v. 53(2): p.191-196, 20054. Gibson, R. W.&Pickett, J. A. (14 April 1983), "Wild potato repels aphids by release of aphid alarm pheromone", Nature 302 (5909): 608–609, doi:10.1038/302608a0, http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v302/n5909/abs/302608a0.html
5. Avé, D. A., Gregory, P., Tingey, W. M. (July 1987), "Aphid repellent sesquiterpenes in glandular trichomes of Solanum berthaultii and S. tuberosum", Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata 44: 131–138, doi:10.1007/BF00367620
6. Ernest Small Culinary herbs, National Research Council Canada, 2006, ISBN 0660190737 p. 288
7. The Aromatic Plant Project http://www.aromaticplantproject.com/articles_archive/azulene_chamomile.html